Antimalware Service Executable – What Is It And How To Disable It?

Microsoft’s embedded antivirus software, known as Windows Defender, ensures that measures are in place to safeguard systems at all times. Even if you haven’t installed an antivirus solution on a Windows operating system or have out-of-date software running, your system will automatically install Windows Defender. One crucial functionality that accompanies this system is the Antimalware Service Executable.
Windows Defender's background service, an executable service file, runs in the background and continuously checks the system for malware, typically when each file is accessed. The executable will perform background scans to detect malicious content and update antivirus definitions as they’re released.
As useful as this feature is, it may hog memory and disk space. Therefore, you might want to disable it. Here’s how you can disable this to save your device’s resources.
Antimalware Service Executable In Detail
If you have Windows Defender, you’ll find it among the background processes, within the Antimalware Service Executable, in the executable file msmpeng.exe. This executable allows the Windows Defender application to monitor your system continuously for potential threats. It aids in providing all-time, well-rounded protection against malware and other forms of cyberattacks.
In general, the process keeps running in the background and detects anything potentially harmful. Additionally, it keeps continuously scanning the device for worms and viruses. Thus, causing high CPU usage that’s very disproportionate. Since the executable relies on the CPU mostly for its functioning, it might lead to delays, lags, and other miscellaneous disruptions while running. As much as this application might provide real-time protection, it takes a toll on the system’s overall performance.
How Do I Stop Antimalware Service Executable From Using My Memory?
It protects your system from various cyber-attacks, and in the process of providing real-time protection, it uses up a ton of memory. When the executable file is running, it triggers a detailed scan. That’s why you’ll experience issues like lagging and delay in processing.
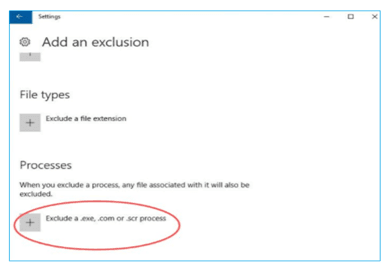
You can try the following fixes to prevent the Antimalware Service Executable from high memory consumption of your device(s):